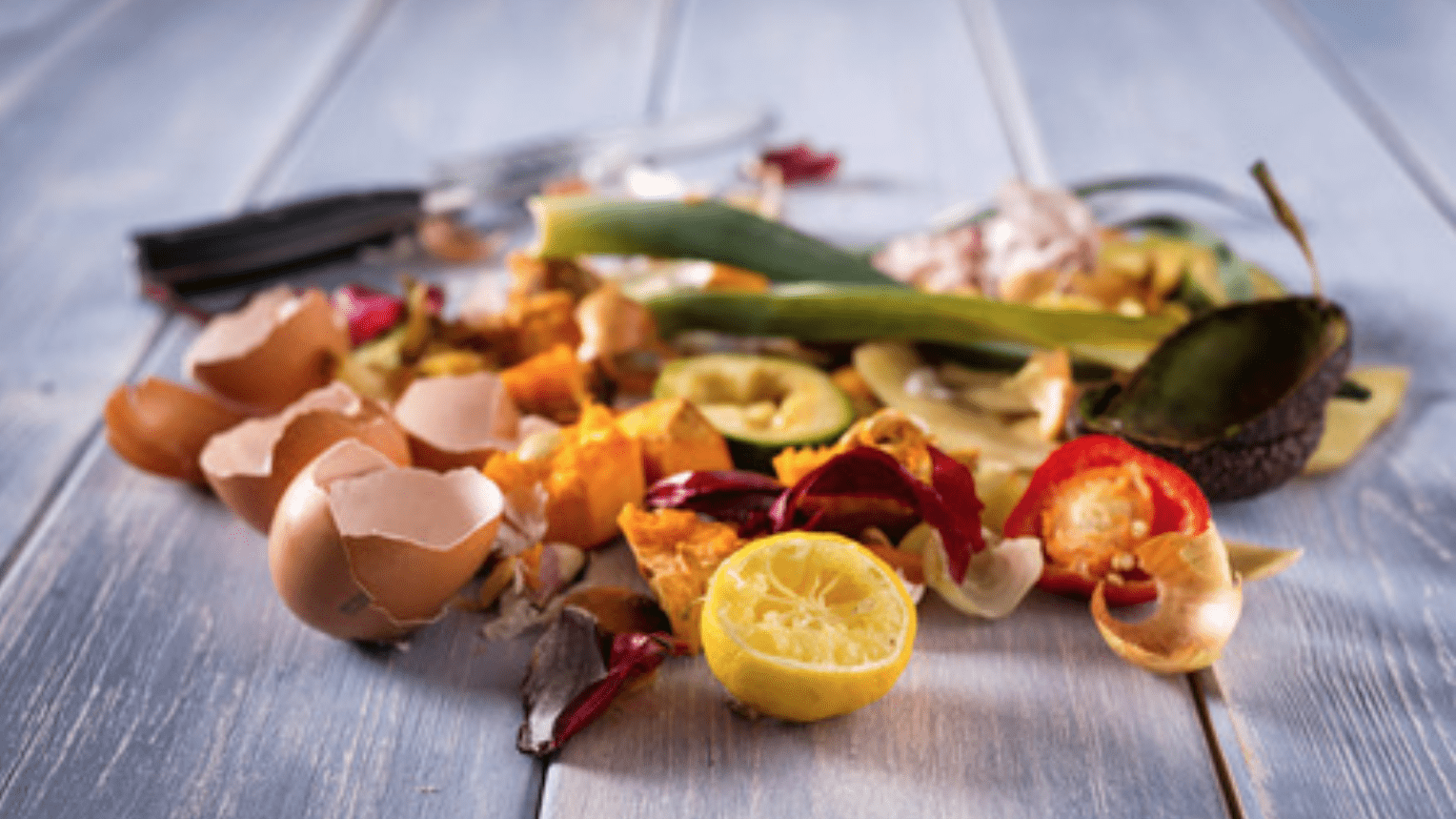
What is biowaste?
Each year, French households generate 18 million tons of biowaste, or one-third of their waste. In 2017, 4.2 million tons of organic waste were collected in French waste collection centers. A bad habit, which does not allow to valorize this organic waste. But what is a bio-waste? Why and how to sort it? How to valorize them in company?
What is biowaste?
Food waste and other biodegradable natural wastes are considered as biowaste. They are biodegradable if they can be transformed into carbon dioxide or methane, water and biomass by the action of micro-organisms that use this organic matter as nutrients.
Biowaste is registered on the list of non-hazardous waste: its management must meet specific obligations of prevention, sorting and recovery.
They are categorized into different families:
- Kitchen and table waste.
- Commercial or food market waste (from fruit and vegetable stalls, florists, butchers and fishmongers).
- Green waste from gardens or parks.
- Used cooking oil.
Why separate biowaste from other waste?
Conventional treatment of biowaste such as landfilling, incineration or burial has a significant negative impact on our environment.
Landfilling causes food waste to ferment, releasing methane into the atmosphere. This greenhouse gas is 25 times more dangerous than CO2 for global warming. It is one of the main elements responsible for global warming.
Incineration releases CO2. Every year, one million tons of biowaste are burned in the open air. To give you an idea, 50 kg of burned plants emit as much fine particles as a diesel car driven 13,000 km. Moreover, burning organic waste is completely unnecessary. Consisting of 60 to 90 % water, this waste is not energetically recovered.
Landfilling biowaste poses a threat to soil and water. Organic resources produce residual liquids, called leachate. They come from the percolation of rainwater and water from organic waste. Discharged into the natural environment around landfills, these liquids, mostly untreated, contain contaminants and toxic substances harmful to animals and plants.
Why sort them?
The proper recycling of biowaste is of great benefit to our environment and to ourselves:

Preserve the soil
With our modes of production and consumption, intensive agriculture and cattle breeding, the earth is constantly solicited without ever having the time to regenerate itself. This leads to the poverty of the soil in organic matter. The treatment of biowaste by composting or methanization allows to:
- Preserve and fertilize the soil
- Reinforce soil stability and increase its porosity
- Retain water
- Improve air circulation, thus promoting plant rooting.
Thanks to this, it is not necessary to resort to the use of synthetic fertilizers. Especially since the production of these fertilizers is based on the use of phosphorus and potassium, two non-renewable resources that cannot be found in France.

Creating energy
Through the process of composting and methanization, biowaste can produce electricity, heat and biofuel, thus becoming a renewable energy. In this way, biodegradable waste replaces fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal), resources that accelerate global warming and have harmful consequences on health.

Reduce costs
Biowaste recovery saves expensive waste management costs. Here are some of the benefits:
- Less energy consumption for transportation.
- Less GHG emissions generated by waste collection vehicles.
- Reduction of landfill and incineration with all their negative impacts.

Moving towards a circular economy
The sorting of organic waste allows us to stop the linear model of “make, consume, throw away”, to move towards a circular economy where each product can benefit from a second life cycle while limiting its impact on the environment. In concrete terms, organic products return to nature and create a new production cycle.
In addition, separate collection of bio-waste increases the sorting efficiency of other waste streams.
How can they be valued in the company?
Sorting must become a reflex for your employees. For this, it is necessary to facilitate them by placing sorting bins on the floors of the offices in a strategic way. Generally, this kind of waste is sorted near the canteens and refectories or in the break rooms.
For a more complete answer, watch our interview with Moulinot, specialist in the sorting and collection of food waste.
The main thing
Biowaste is food waste and other biodegradable natural waste. It can be transformed into fertilizer and/or green energy through composting or methanization. Biowaste needs a specific treatment. Incinerating, burying or dumping it has a considerable negative impact on our environment. Indeed, the CO2 generated during these processes is one of the main elements responsible for global warming. By sorting them correctly, we preserve the soil, create energy and a circular economy and reduce costs. Discover the interview of Moulinot, specialist in the sorting and collection of biowaste, on the subject “How to recover your biowaste?